Chapter – 1
Population: Distribution, Density, Growth and Composition
In this post, we have given the Important Questions of Class 12 Geography Chapter 1 (Population: Distribution, Density, Growth and Composition) in English. These Important Questions are useful for the students who are going to appear in class 12 board exams.
| Board | CBSE Board, UP Board, JAC Board, Bihar Board, HBSE Board, UBSE Board, PSEB Board, RBSE Board |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 12 |
| Subject | Geography |
| Chapter no. | Chapter 1 |
| Chapter Name | (Population: Distribution, Density, Growth and Composition) |
| Category | Class 12 Geography Important Questions in English |
| Medium | English |
Chapter – 1, (Population: Distribution, Density, Growth and Composition)
1 Mark Questions
Q1 The average density of the population of India (2011) is per km.
(a) 216
(b) 382
(c) 221
(d) 382
Q2 Which the state of India has the highest population?
(a) Uttar Pradesh.
(b) Maharashtra.
(c) Bihar.
(d) West Bengal.
Q3 Choose the correct option:
- Hindus are largest religious group in India.
- Muslims are largest minority group in India.
(a) Statement I is correct
(b) Both are correct
(c) Statement II is correct
(d) Both are incorrect.
Q4 Which state has the highest % rural population?
(a) Uttar Pradesh
(b) Himachal Pradesh
(c) Bihar
(d) Jammu& Kashmir
Q5 State having lowest sex ratio in India-
(a) Punjab
(b) Bihar
(c) Haryana
(d) Chhattisgarh
Q6 State has highest percentage of population in urban area?
(a) Goa
(b) Maharashtra.
(c) Karnataka.
(d) Punjab.
3 Marks Short Answer
Q1 Write the name of three types of density. Which type density important for India and Why?
Ans:
(a) Arithmetic Density
(b) Physiological Density
(c) Agricultural Density
Agriculture density is important for India. Most of Indian population depends on agriculture.
Q2 Distinguish between rural and urban population composition.
Ans:
Rural Population
- Agriculture is the main occupation.
- The rural population is not provided with modern facilities
- Informal relation
- The density of population is low in rural areas.
Urban Population
- Manufacturing and service are the main occupation.
- Modern facilities are available in the urban centers.
- Formal relation
- Very high density of population in urban areas.
Q3 State the distributional patterns of sex ratio in the country.
Ans :
- Sex ratio of India in 2011 is 940 while it was 972 in 1991.
- Sex ratio high is in rural areas.
- Kerala has the highest sex ratio of 1084
- 17 states and 2 Union territories have sex ratio higher than national average.
- Sex Ratio decline from south to north and from east to west.
Q4 What is population density? Mention factors responsible for uneven distribution of population.
Ans: No. of persons living per unit area is known as density of population. Physical factor- landform, availability of water, climate Socio –economic factor – Industrialization, Urbanization and Historical- factors are responsible for uneven distribution of population.
Q5 On the basis of economic status, India’s population is divided into the following three categories.
Ans:
- Main Workers: A person who works for at least 183 days in a year. They are the main contributors to a nation’s GDP.
- Marginal Workers: A person who works for less than 183 days in a year. They are mostly engaged in the agricultural sector.
- Non-Worker: A person who does not work for his livelihood. They are dependent on the working population for their needs.
5 Marks Questions
Q1 India has highly uneven patterns of population distribution. Justify this statement with four facts.
Ans. India has a highly uneven pattern of population distribution.
- Uttar Pradesh has the highest total population followed by Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal and Andhra Pradesh.
- Top 10 states together have about 76 per cent of the total India’s population.
- On the other hand, population is very small in the states like Jammu & Kashmir, Arunachal Pradesh and Uttaranchal even though they are large states.
- Rajasthan, Jharkhand and Peninsular States have moderate to high proportion of population.
Q2 Explain four distinct phases of growth of India’s population.
Ans. There are four distinct phases of growth identified:
Phase I:
- The period from 1901-1921 is referred to as a period of stagnant or stationary phase of growth of India’s population
- In this period growth rate was very low, even recording a negative growth rate during 1911- 1921.
- Both the birth rate and death rate were high keeping the rate of increase low.
- Poor health and medical services, illiteracy of people at large and in -efficient distribution system of food and other basic necessities were largely responsible for a high birth and death rates in this period.
Phase II:
- The decades 1921-1951 are referred to as the period of steady population growth.
- An overall improvement in health and sanitation throughout the country brought down the mortality rate.
- At the same time better transport and communication system improved distribution system.
- The crude birth rate remained high in this period leading to higher growth rate than the previous phase.
Phase III:
- The decades 1951-1981 are referred to as the period of population explosion in India,
- It was caused by a rapid fall in the death rate but a high birth rate.
- The average annual growth rate was as high as 2.2 per cent.
- High birth rate was due to developmental activities and growing economy which improved living condition of people.
- Beside it, due to increased international immigration from Tibet, Bangladesh, Nepal and Pakistan growth rate was high.
Phase IV:
- After 1981 till present, the growth rate has started slowing down gradually.
- It is due to decline in crude birth rate.
- It is also due to an increase in the mean age at marriage, improved quality of life particularly education of females in the country.
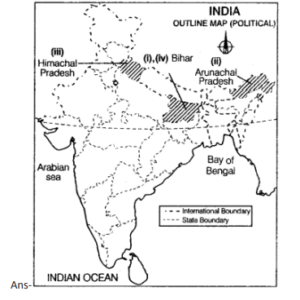
Map work
Q1 Locate and label the following on the given political outline map of India with appropriate symbols.
(i) The state having the highest density of population.
(ii) The state with the lowest density of population.
OR
The state having the lowest density of population.
(iii) The state with the highest percentage of the rural population.
(in) The state having the lowest literacy rate in India.
We hope that Class 12 Geography Chapter 1 (Population: Distribution, Density, Growth and Composition) Important Questions in English helped you. If you have any queries about class 12 Geography Chapter 1 (Population: Distribution, Density, Growth and Composition) Important Questions in English or about any other notes of class 12 Geography in English, so you can comment below. We will reach you as soon as possible…


