Chapter – 2
Migration: Types, Causes and Consequences
In this post, we have given the Important Questions of Class 12 Geography Chapter 2 (Migration: Types, Causes and Consequences) in English. These Important Questions are useful for the students who are going to appear in class 12 board exams.
| Board | CBSE Board, UP Board, JAC Board, Bihar Board, HBSE Board, UBSE Board, PSEB Board, RBSE Board |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 12 |
| Subject | Geography |
| Chapter no. | Chapter 2 |
| Chapter Name | (Migration: Types, Causes and Consequences) |
| Category | Class 12 Geography Important Questions in English |
| Medium | English |
Chapter – 2, (Migration: Types, Causes and Consequences)
1 Mark Questions
Q1 Which one of the following streams is the main reason for female migration in India?
(a) Education
(b) Business
(c) Work & Employment
(d) Marriage
Q2 When was the first Census of India conducted?
(a) 1881
(b) 1891
(c) 2001
(d) 1971
Q3 Which one of the following states receives maximum number of immigrants?
(a) Uttar Pradesh
(b) Delhi
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Bihar
Q4 Which of the following is not a problem of migration to urban areas?
(a) Congestion
(b)Development of slums
(c) Development of inferior colonies
(d) Reduction in life expectancy
Q5 Which of the following is not included under pull factors of migration?
(a) Natural disaster
(b) Unemployment
(c) Pleasant climate
(d) Lack of facilities
Q6 Which one of the following streams is dominated by male migrants in India?
(a) Rural to Rural
(b)Urban- Rural
(c) Rural- Urban
(d) Urban –Urban
Q7 Which state of India receives highest amount of remittance from Migration?
(a) Uttar Pradesh
(b) Punjab
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Bihar
Q8 What are the causes of Migration?
(a) Poverty
(b) Health
(c) Drought
(d) All of these
Q9 During colonial period migrants were taken to the Mauritius, Caribbean islands under which act?
(a) Population Act
(b)Labour Act
(c) Girmit Act
(d) Migration Act
Q10 During third wave of migration, the migrants was comprised mainly……………….
(a) Plantation workers
(b) Factory workers
(c) Traders
(d) Professionals
Q11 “Family planning, Girls education gets diffused from urban to rural areas” is an example of which type of consequences of migration?
(a) Social consequences
(b) Demographic consequences
(c) Economic consequences
(d) Environmental consequences
Source Diagram-Based Questions
Q12 Study the graph given below and answer any three of the following Questions:
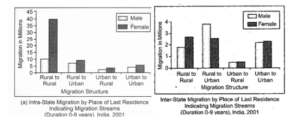
(i) In Intra-state migration, which gender has the highest rate of migration and in which direction?
(A) Male from rural to Urban
(B) Female from Urban to rural
(C) Male from Urban to Urban
(D) Female from Rural to Rural
(ii) In Inter-state migration, which gender has the highest rate of migration and in which direction?
(A) Male from rural to Urban
(B) Female from Urban to rural
(C) Male from Urban to Urban
(D) Female from Rural to Rural
(iii) In which form of migration seems to equal amongst male and female?
(A) Rural to Rural
(B) Urban to Rural
(C) Urban to rural
(D) Rural to Urban
(iv) Which one of the following is the main reason for male migration in India?
(A) Business
(B) Education
(C) Work and employment
(D) Marriage
Q13 Study the graph given below and answer any three of the following Questions:
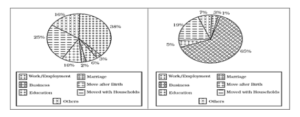
(i) Which one of the following is the main reason for female migration in India?
(A) Business
(B) Education
(C) Work and employment
(D) Marriage
(ii) Which one of the following is the main
(A) Business
(B) Education
(C) Work and employment
(D) Marriage
(iii) Which component is responsible for minimum male migraUon
(A) Education
(B) Work and employment
(C) Marriage
(iv) Which component is responsible for minimum female migration
(A) Business
(B) Education
(C) Work and employment
(D) Marriage
Ans: work and employment
3 Marks Questions
Q1 Explain the causes of migration with reference to India.
Ans: These reasons can be put into two broad categories:
1. Push factor, these cause people to leave their place of residence or origin. In India people migrate from rural to urban areas mainly due to poverty, high population pressure on the land, lack of basic infrastructural facilities like health care, education, etc.
Apart from these factors, natural disasters such as, flood, drought, cyclonic storms, earthquake, tsunami, wars and local conflicts also give extra push to migrate.
2. Pull Factors, which attract the people from different places. there are pull factors which attract people from rural areas to cities. The most important pull factor for majority of the rural migrants to urban areas is the better opportunities, availability of regular work and relatively higher wages. Better opportunities for education, better health facilities and sources of entertainment, etc., are also quite important pull factors.
Q2. What is migration? Distinguish between life time migrants and migrants by last residence.
Ans: Movement of people from one place to another is called migration
- Place of birth, if the place of birth is different from the place of enumeration (known as lifetime migrant);
- Place of residence, if the place of last residence is different from the place of enumeration (known as migrant by place of last residence).
Q3 What are the streams of migration? Why is it important?
Ans: Migration can be permanent, temporary or seasonal. There are generally four streams of migration.
- Rural to rural
- Rural to urban
- Urban to rural
- Urban to Urban
Migration is important because it is a spontaneous effort to attain a better balance between resources and population. There are push and pull factors working together behind migration.
Q4 What are the environmental consequences of migration? Explain.
Ans:
- The overcrowding of people due to rural-urban migration has put pressure on the existing social and physical infrastructure in the urban areas.
- This ultimately leads to the unplanned growth of urban settlement and the formation of slums shanty colonies.
- Due to the over-exploitation of natural resources, cities are facing the acute problem of depletion of groundwater, air pollution, and disposal of sewage and management of solid wastes.
5 Marks Questions
Q1 Discuss the consequences of international migration in India.
Ans:
- A major benefit for the source region is the remittance sent by migrants.
- Remittances from the international migrants are one of the major sources of foreign exchange.
- In 2002, India received US $ 11 billion as remittances from international migrants. Punjab, Kerala and Tamil Nadu receive very significant amount from their international migrants.
- The loss of human resources particularly highly skilled people is the most serious cost.
- The market for advanced skills has become truly a global market and the most dynamic industrial economies are admitting and recruiting significant proportions of the highly trained professionals from poor regions.
- Consequently, the existing underdevelopment in the source region gets reinforced.
Q2 Discuss the major consequences of migration with reference to India.
Ans:
Economic Consequences:
- A major benefit for the source region is the remittance sent by migrants.
- Remittances from the international migrants are one of the major sources of foreign exchange.
- The amount of remittances sent by the internal migrants is very meager as compared to international migrants, but it plays an important role in the growth of economy of the source area.
- Remittances are mainly used for food, repayment of debts, treatment, marriages, children’s education, agricultural inputs, construction of houses, etc.
Demographic Consequences:
- Migration leads to the redistribution of the population within a country.
- Age and skill selective out migration from the rural area have adverse effect on the rural demographic structure.
- high out migration from Uttarakhand, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Eastern Maharashtra have brought serious imbalances in age and sex composition in these states.
Social Consequences:
- Migrants act as agents of social change. The new ideas related to new technologies, family planning, girl’s education, etc. get diffused from urban to rural areas through them.
- Migration leads to intermixing of people from diverse cultures. It has positive contribution such as evolution of composite culture and breaking through the narrow considerations and widens up the mental horizon of the people at large.
- Negative consequences such as anonymity, which creates social vacuum and sense of dejection among individuals. Continued feeling of dejection may motivate people to fall in the trap of anti-social activities like crime and drug abuse.
Environmental Consequences:
- Overcrowding of people due to rural-urban migration has put pressure on the existing social and physical infrastructure in the urban areas.
- This ultimately leads to unplanned growth of urban settlement and formation of slums shanty colonies.
- due to over-exploitation of natural resources, cities are facing the acute problem of depletion of ground water, air pollution, disposal of sewage and management of solid wastes.
Other Consequences:
- In the rural areas, male selective out migration leaving their wives behind puts extra physical as well mental pressure on the women.
- the loss of human resources particularly highly skilled people is the most serious cost.
We hope that Class 12 Geography Chapter 2 (Migration: Types, Causes and Consequences) Important Questions in English helped you. If you have any queries about class 12 Geography Chapter 2 (Migration: Types, Causes and Consequences) Important Questions in English or about any other notes of class 12 Geography in English, so you can comment below. We will reach you as soon as possible…


