Chapter – 4
India’s External Relations
In this post, we have given the Important Questions of Class 12 Political Science Chapter 4 (India’s External Relations) in English. These Important Questions are useful for the students who are going to appear in class 12 board exams.
| Board | CBSE Board, UP Board, JAC Board, Bihar Board, HBSE Board, UBSE Board, PSEB Board, RBSE Board |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 12 |
| Subject | Political Science |
| Chapter no. | Chapter 4 |
| Chapter Name | (India’s External Relations) |
| Category | Class 12 Political Science Important Questions in English |
| Medium | English |
Chapter 4 India’s External Relations
One Marker Questions
Q1. Which article of Indian constitution lays down some Directive Principles of State Policy on promotion of international peace and security?
- Article 351
- Article 51
- Article 368
- Article 68
Ans. b) Article 51
Q2. Write full form of NPT.
Ans. Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty
Q3. Fill in the blanks:-
China conducted a nuclear test in
- October 1962
- October 1964
- October 1968
- November 1964
Ans. b) October 1964
Q4. To whom did India provide political asylum in 1959?
Ans. Dalai Lama
Q5. Tashkent agreement is signed between these two countries?.
- Pakistan and India
- China and India
- India and USSR
- India and USA
Ans. a) Pakistan and India
Q6. Which state is called NEFA?
- Assam
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Andhra Pradesh
- Sikkim
Ans. b) Arunachal Pradesh
Q7. When did India conduct its first nuclear test?
- 1974
- 1978
- 1992
- 1998
Ans. a) 1974
Q8. Which of the following is not a correct statement regarding India’s Nuclear doctrine:
- The basic principle of India’s nuclear doctrine is “No First Use“.
- Nuclear weapons will only be used in retaliation against a nuclear attack on the Indian Territory or on Indian forces anywhere.
- India will use nuclear weapons against non-nuclear countries.
- India did it first Nuclear Test in the year 1974.
Ans. India will use nuclear weapons against non-nuclear countries.
Two Marker Questions
Q1. How Myanmar is important to India?
Ans.
- Myanmar is significant in the context of our “Act East” policy. Myanmar is India’s gateway to South -East Asia.
- Myanniar is potentially an important partner in the energy sector as future offshore gas can be piped to India.
Q2. Why does India refuse to sign NPT and CTBT?
Ans. India has opposed the NPT and CTBT since they were selectively applicable to the non-nuclear powers and legitimised the monopoly of the five nuclear weapon powers.Thus, India opposed the indefinite extension of the NPT in 1995 and also refused to sign the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT).
Q3. Why did India sign a 20 year Treaty of Peace and Friendship with the , Soviet Union?
Ans. In order to counter the US- Pakistan- China axis, India signed a twenty-year Treaty of Peace and Friendship with the Soviet Union in August 1971. The treaty assured India of Soviet support if the country faced any attack.
Q4. Which river water treaty was signed between India and Pakistan? Who played the role of the mediator?
Ans. A long term dispute about the sharing of river waters was resolved through mediation by the World Bank.The India- Pakistan Indus Water Treaty was signed by Nehru and General Ayub Khan in 1960.
Q5. What was the Kargil conflict?
Ans. In 1999, several points of the Indian side of LOC in the Mashkoh,Dras,Kaksar and Batalik areas were occupied by Mujahideens. Indian Army suspected of Pakistan’s army. This led to confrontation between two countries, which is known as the Kargil conflict.
Four Marker Questions
Q1. Describe the Nuclear Policy of India.
Ans. Building and maintaining a credible minimum deterrent; A posture of “No First Use” nuclear weapons will only be used in retaliation against a nuclear attack on Indian territory or on Indian forces anywhere; Nuclear retaliation to a first strike will be massive and designed to inflict unacceptable damage.
Q2. lndia’s relations with Russia are considered as an important aspect of India’s Foreign Policy. Explain.
Ans.
- India’s relations with Russia are strong and embedded in a history of mutual faith and matched by popular perceptions.
- Both share a vision of multipolar world order.
- Both believe that International conflicts and disputes should be negotiated through bodies like the UN.
- More than 80 bilateral agreements have been signed as part of the Indo- Russian strategic agreement of 2001.
Q3. Describe India’s relation with Israel.
Ans. India announced its recognition of Israel on September 17, 1950. Soon thereafter, the Jewish Agency established an immigration office in Bombay. This was later converted into a Trade Office and subsequently a Consulate. Embassies were opened in 1992 when full diplomatic relations were established.
Q4. What was the Tibet issue?
Ans. In 1950, China took over control of Tibet. Large sections of the Tibetan population oppose this takeover.In 1958, there was an armed uprising in Tibet against China occupation. This was suppressed by the Chinese forces. In 1959, the Dalai Lama crossed over into the Indian border and sought Asylum which was granted. The Chinese government strongly protested against this.
Five Marker Questions
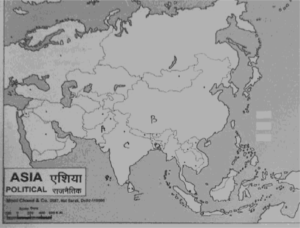
Q1. In the given map five countries have been marked as A,B,C,D and E. Identify them on the basis of the information given below and write their correct names in along with their serial number of the information used and the concerned alphabets as per the following format:-
|
S. No. |
Concerned alphabet |
Name of the state |
|
1) |
|
|
|
2) |
|
|
|
3) |
|
|
|
4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ans.
|
S.No. |
Concerned alphabet |
Name of the state |
|
1) |
E |
Sri-Lanka |
|
2) |
|
India |
|
3) |
D |
Bangladesh |
|
4) |
B |
China |
|
5) |
A |
Pakistan |
Six Marker Questions
Q1. Do you agree with the statement that ‘The Foreign Policy of Independent India has pursued the dream of a peaceful world’? Justify your answer with two suitable arguments.
Ans. The foreign policy of independent India vigorously pursued the dream of a peaceful world by.
- advocating the policy of nonalignment by reducing the cold war tensions. India did not join either of the two camps during the cold war era. India wanted to keep away from the military alliances led by the US and Soviet Union against each other. India advocated non-alignment as the ideal foreign policy approach.
- by contributing human resources to the UN peacekeeping operations.
Q2. Explain in detail the result of the 1962, 1965 and 1971 war on India.
Ans.
- A decisive victory in the 1971 war led to national jubilation.
- After the 1971 war , Assembly elections in most States took p1ace,bringing large majorities to the Congress Party.
- Conflicts with the neighbours derailed the five year plans.
- The resources were diverted to the defence sector especially after 1962.
- The Department of Defence Production was established in November 1962.
- The Department of Defence Supplies was established in November 1965.
- The third Five year Plan(1961-66) was affected and it was followed by three annual plans.
- The fourth five year plan could be initiated only in 1969.
- India’s defence expenditure increased enormously after the Wars.
Q3. Give any three suitable arguments in favour of India being a staunch supporter of the decolonization process and in the firm opposition to racialism.
Ans.
- India convened the Asian relations conference in March 1947, five months ahead of attaining its independence.
- India made earnest efforts for the early realisation of freedom of Indonesia from the Dutch colonial.
- India was a staunch supporter of the decolonization process and firmally opposed racism, the especially Apartheid in South Africa. The Afro -Asian Conference held in the Indonesia city Bandung in 1955 is an example of India’s efforts.
We hope that Class 12 Political Science Chapter 4 (India’s External Relations) Important Questions in English helped you. If you have any queries about class 12 Political Science Chapter 4 (India’s External Relations) Important Questions in English or about any other notes of class 12 Political Science in English, so you can comment below. We will reach you as soon as possible…


