Chapter – 7
Physiology and Injuries in Sports
In this post, we have given the Important Questions of Class 12 Physical Education Chapter 7 (Physiology and Injuries in Sports) in English. These Important Questions are useful for the students who are going to appear in class 12 board exams.
| Board | CBSE Board, UP Board, JAC Board, Bihar Board, HBSE Board, UBSE Board, PSEB Board, RBSE Board |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 12 |
| Subject | Physical Education |
| Chapter no. | Chapter 7 |
| Chapter Name | (Physiology and Injuries in Sports) |
| Category | Class 12 Physical Education Important Questions in English |
| Medium | English |
Short Answer Type Questions (2 Mark each)
Q1. Discuss the physiological factor and determine endurance as a component of Physical Fitness.
Ans.
Aerobic capacity:
- Oxygen intake
- Oxygen uptake
- Oxygen transport
- Energy Reserve
Anaerobic capacity :
- Storage in the body of ATP and CP (phosphagen stock)
- Buffer capacity -in muscles lactic acid accumulation ineffective
- Endurance of lactic acid
- VO2 max. This is the quantity of oxygen, that active muscles use during exercise in one minute.
Q2. Define soft tissue injuries in sports. Write its preventive measures.
Ans. Soft tissue refers to tissues that connect, support, or surround other structures and organs of the body the muscles, tendons, ligaments, fascial, nerves, fibrous tissue, blood vessels, etc. soft tissue injuries involve injuries to muscles, ligaments, and tendons in the body.
Preventive measures of soft tissue injuries:
- Proper warming up
- Proper conditioning of body
- Scientific equipment & facilities
- Clean & plain surfaces of playgrounds
- Knowledge of rules & regulations of sports events.
- Actively & alert participation during the sports training & competition.
- Fatigue, sickness & injuries’ condition to avoid participation in the sports training.
Q3. What do you mean by dislocation in joints? Explain any two dislocations In the body.
Ans. Dislocation
A dislocation is a separation of two bones where they meet at a joint. Joints are areas where two or more bones come together.
1. Dislocation of Lower Jaw: Generally, it occurs when the chin strikes any other object. It may also occur if the mouth is opened excessively.
Example: Boxing, MMA, etc.
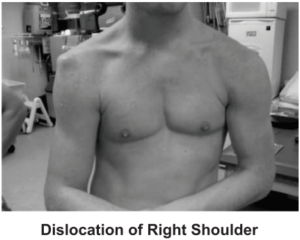
2. Dislocation of Shoulder Joint: Dislocation of the shoulder joint may occur due to a sudden jerk or a fall on a hard surface. The end of the humerus comes out from the socket.
Example: Judo, Wrestling, etc.
Q4. Explain the objectives of first aids.
Ans. It is immediate & temporary care given to a victim of an accident or sudden illness before the services of a physician is obtained.
Objectives of first aid
- To preserve life
- To alleviate pain & suffering
- To prevent the condition from worsening
- To promote recovery
- To procure early medical aid
Short Answer Type Questions (3 Mark each)
Q.1 Discuss the physiological factor and determine the strength as a component of physical Fitness.
Ans.
- 1. Muscle size: Bigger and larger muscles can produce more force. Males have larger muscles than females so the size of muscles and strength can be improved with the help of weight training.
- 2. Body weight: The individuals who are heavier are stronger than the individuals who are lighter for example the heavier weight lifters than the gymnastics or other game players.
-
3. Muscle composition: The muscles which have more percentage of fast twitch fibers can produce more strength while the slow twitch fibers are not capable to contract faster but they are capable of contracting for a longer duration. The percentage of fast twitch fibers and slow twitch fibers is genetically determined and can not be changed through training.
-
4. Intensity of the never impulse: When a stronger nerve impulse from the central nervous system excites more motor units, the muscles will contract more strongly or it can side that the muscle will contract more strongly or muscle will produce more force or strength.
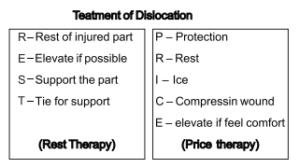
Q2. Write the signs & symptoms and treatment of dislocation.
Ans. Discuss the preventive measures of dislocation.
Signs and symptoms: A dislocated joint may be
- Accompanied by numbness or tingling at the joint or beyond n.
- Intensely painful, especially if you try to use the joint or put weight on it.
- Limited in movement at injured part.
- Swollen or bruised.
- The injured part may be directly visible
Prevention of Dislocation of Joints :
- An adequate warm-up should be performed prior to any physical activity.
- Proper conditioning should be done in the preparatory period.
- Stretching exercises should be included in the warm-up.
- Players should be careful and alert during practice and competition.
- Protective equipment should be used as per the requirement of the games/sports.
- Practice should be discounted during fatigue.
- Players should have good anticipation and concentration power.
- Always obey the rules and regulations.
- Proper cooling down after physical activities.
Q3. Enumerate the types of fractures. Write briefly about any three types of fracture.
Ans. Types of Bone Fractures
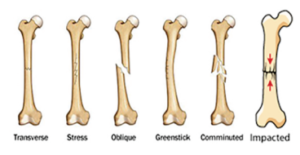
- Greenstick Fracture: An incomplete fracture in which a bone bends and cracks. This type of fracture usually occurs in children because their bones are soft and flexible.
- Transverse Fracture: A fracture at a right angle o the bone’s axis or a straight break right across a bone.
- Oblique Fracture: A fracture occurs when a force is applied diagonally at an angle to a bone’s long axis.
- Impacted Fracture: It is a loss of continuity in the structure of bones. One bone is driven into another bone.
- Stress Fractures: It is a crack in the bone due to high-impact physical activity.
- Comminuted Fracture: A fracture in which the bone is broken into more than two pieces.
Q4. Discuss the causes of fracture.
Ans. The fracture usually occurs due to a high impact on the bone. It can be caused by overuse.
The most common causes of fracture are:
- In such sports events where there Is a high impact.
- Traumatic, forceful, and unnatural movements of the body.
- Prolong long-distance walking & running.
- Suddenfalls onhard surface.
- Direct strike or hit with any solid sports equipment.
- Osteoporosis.
Long Answer Type Question (5 Marks)
Q1 Discuss how physiological Factors determine flexibility.
Ans.
- 1. Muscle strength:- The muscle should have a minimum level of strength to make the movement, especially against gravity or external force.
- 2. Joint structure:- There are different types of joints in the human body, some of the joints intrinsically have a greater range of motion than others. For example. The ball and socket joint of the shoulder has the greatest range of motionIncomparisonto the knee joint.
- 3. Internal environment:- Internal environment of the athlete influences flexibility. For example-warm bath increases body temperature and flexibility whereas 10 minutes outside stay in 10°c temperature reduces the body temperature and flexibility.
- 4. Injury:- Injuries to connecting tissues and muscles can lead to thickening or fibroin in the affected area. Fibrous tissues are less elastic and can lead to limb shortening and lead reduce flexibility.
- 5. Age and gender:- Flexibility decreases with the advancement of age. However, it is trainable. It can be enhanced with the help of training, as strength and endurance are enhanced. Gender also determines flexibility. Females tend to be more flexible than males.
- 6. Active and sedentary lifestyle:- Regular Activities enhance flexibility, whereas inactive individual loses flexibility due to the soft tissues and joints shrinking and losing extensibility.
- 7. Heredity: Bony structures of joint length and flexibility of the joint capsules and surrounding ligaments are genetic and can be altered by stretching programs.
Q.2. Describe the physiological factor that determines the speed.
Ans.
- 1. Explosive strength: For every quick and explosive movement, explosive strength is required. Like, a quick punch in boxing can not be delivered if the boxer lacks explosive strength. Explosive strength further depends on muscle composition, muscle size, and muscle coordination.
- 2. Muscle composition: The muscle which has more fast last fibers. They can produce more speed. The muscle composition is genetically determined. We will improve it only by specific training methods.
- 3. Mobility of nervous system: Motorandsensory nerves of the nervous system can be determined by the mobility of the nervous system. By training only we can limit the extent of the mobility of the nervous system because speed is determined to a great extent by genetic factors.
- 4. Elasticity and Relaxing capacity of muscle: Through elasticity of muscle. muscle can move to a maximum range which reduces the Inner hurdles and Isinstrumentalin speeds up the activity. The muscles which get relaxed soon, contract easily.
- 5. Bio-chemical reserves and metabolic Power: For doing the exercises which are done quickly muscles need more energy. This energy in our muscles is obtained through the ATP-PC system. The percentage of power and quantity in ATP and PC can be increased through training.
Q3. Explain the five effects of exercise on the cordio respiratory system.
Ans.
- increase in heart rate:- When an individual starts to exercise, his heart rate increases as per the intensity and duration of exercise.
- Increase in stroke volume:- Stroke volume increases proportionally with exercise intensity. It is measured in ml/beat.
- Increase in cardiac output:- cardiac output increases proportionally with the intensity of exercise measured in liter/ minute.
- Increases in blood flow:- Cardio-vascular can distribute more blood to those tissues which have more demand for oxygen and nutrients.
- Increase in blood pressure:- During the exercise. systolic blood pressure can increase while diastolic blood pressure usually remains unchanged even during intensive exercise.
- Increase in vital capacity:- It is the amount of air that an individual can inhale and exhale with maximum effect. its capacity varies from 3500 cc. Due to exercise, Its capacity increases up to 5500 cc.
- Increase in Residual air volume- Due to regular exercise increases the capacity of residual volume from normal capacity.
- Passive Alveolus becomes Active- Regular exercise activates the unused alveolus because much amount of O2 is required in the prolonged exercise in the daily routine.
- Increase Endurance:- If exercises are performed regularly and for a longer period, it increases endurance. An activity can be done for a longer period without taking any rest.
Q4. List the effects of exercises on the muscular system and explain five in detail.
Ans.
- Increase In the shape of muscles
- Activation of inactive capillaries
- Muscles Remain In tone Position
- Increase in Activenese of fibers
- Correct body posture
- Improves Reaction t me
- Reduction in extra fat
- Increase in strength of connective tissues
- Efficiency in muscle movements
- Delay fatigue
- Enhances body figure
- Exercise prevents disease
1. Muscle Hypertrophy- Due to regular exercise a good growth in the size of muscles.
2. ControlExtra fat- Regular exercise controls the extra fat in the body. Exercises burn extra calories.
3. Delay fatigue- Regular exercise delay fatigue. This fatigue is mainly due to the formation of carbon dioxide, lactic acid, and acid phosphate.
4. Posture- Regular exercise helps in the improvement of body posture from various postural deformities by strengthening muscles.
5. Strength and speed- Regular exercise improves fitness components like Coordination, Power, Balance, Speed, Agility, Reaction Time, Flexibility, and Endurance of Muscles.
Q5. How you will prevent injuries in sports?
Ans. Prevention of sports injuries
Competitive athletes may have difficulty avoiding sports injuries due to the intensity and frequency of their training and competition. However. it is possible to prevent most sports injuries by undertaking the following preventive measures.
1. Proper warming up: Before the start of any practice competition proper warming-up is essential. Sports injuries can be prevented to a greater extent. Proper warming up helps our muscles to gel ready for work.
2. Proper conditioning: Many injuries occur due to weakness of muscles that are not ready to meet the demand of sports. So. getting proper compatibility is a must for muscular power training
load and circumference training weight training circuit training methods which develops Neuro-muscular co ordination among muscles and prevent us from injuries.
3. Balanced diet: Balanced diet helps us (to some extent) prevent Injuries. For example, Intake of calcium, phosphorous, and vitamin D in lots of quantity to meet the demands of muscles and organs to practice activities.
4. Proper knowledge of sports skills: Proper knowledge of sports skills Is necessary for the prevention of Injuries. Players who are fully skilled or have sound knowledge of sports skills can prevent injuries.
5. Use of protective equipment: The use of protective equipment Is necessary for the prevention of sports Injuries. So always, wear protective equipment while playing sports. They provide security to the bodies. For better results, always try to put on high-quality protective equipment.
6. Proper sports facilities: Sports facilities and sports Injuries have relation between them. In fact, sports Injuries can be prevented if there is a high-quality protection sports equipment and proper playgrounds are available for practice and competition.
7. Unbiased officiating: If the team officials take decisions without any bias, Injuries can be minimized. If the officials or referees practice partiality, there may be more changes of Indiscipline among players which leads to injuries. So unbiased officiating can prevent Injuries on sports fields.
8. Avoid overtraining: Physical training should be gradually increased to avoid injury. Exercise should be according to the current status of the physical fitness level of the athletes toIncrease the strength and quality of musicals. Avoid training in which muscles are fatigued or weakened.
9. Use of proper technique: Using proper techniques for playing different sports prevents us from severe sports injuries, such as tendonitis and stress fracture.
10. Obeying the sport’s rules: Obeying tile sports rules is also helpful in preventing sports injuries to a greater extent.
11. Proper cooling down: After regular practice or competition, cooling down is equally important as warming up before practice or competition. Cooling down should be done properly.
12. Avoid training when you are tired.
13. Increase your consumption of carbohydrates during periods of heavy training.
14. Any increase in training load should be preceded by an increase in strengthening.
15. Treat even seemingly minor injuries very carefully to prevent them from becoming a big problem.
16. Proper atmosphere & surface use training & competition.
17. Proper Protection from infection areas during training or competition
18. Pay attention to hydration and nutrition during HO training or competition.
19. Use proper clothes, shoes, and equipment during the training on different surfaces & environments.
We hope that Class 12 Physical Education Chapter 7 (Physiology and Injuries in Sports) Important Questions in English helped you. If you have any queries about class 12 Physical Education Chapter 7 (Physiology and Injuries in Sports) Important Questions in English or about any other notes of class 12 Physical Education in English, so you can comment below. We will reach you as soon as possible…


