Chapter – 5
Natural Vegetation and Wild Life
In this post, we have given the Important Questions of Class 9 Social Science Chapter 5 (Natural Vegetation and Wild Life) in English. These Important Questions are useful for the students who are going to appear in Class 9 exams.
| Board | CBSE Board, UP Board, JAC Board, Bihar Board, HBSE Board, UBSE Board, PSEB Board, RBSE Board |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 9 |
| Subject | Social Science |
| Chapter no. | Chapter 5 |
| Chapter Name | (Natural Vegetation and Wild Life) |
| Category | Class 9 Social Science Important Questions in English |
| Medium | English |
1 Mark Questions:
Q1. Name any two trees found in tropical rain forest?
Ans. Ebony, Mahogany, Rosewood, Rubber, Cinchona
Q2. Which vegetation is important for commercial point of view?
Ans. Tropical deciduous forest.
Q3. In which state of India Asiatic Lion is found?
Ans. Gujarat
Q4. In which state Simlipal biosphere reserve is situated?
Ans. Orissa
Q5. When was the Wild Life Protection Act passed in India?
Ans. 1972
Q6. Which type of forest is affected by the tides?
Ans. Mangrove forest
Q7. Name any two types of medicinal plant.
Ans. Neem, Tulsi
Q8. What is natural vegetation?
Ans. Natural vegetation refers to a plant community which has grown naturally without human intervention for a long time.
Q9. Why natural vegetation is called “virgin vegetation”?
Ans. As natural vegetation has grown without human aid and has been left undisturbed for long time, they are also referred as virgin vegetation.
Q10. What is Ecosystem?
Ans. The system of interaction among biotic component and their interaction with abiotic component of a particular area is called Ecosystem. Eg. Pond ecosystem, river ecosystem, lake, forest, grassland etc.
Q11. Give any two products of rain forest.
Ans. Timber, rubber, medicine(cinchona)
Q12. A person has reached in a forest where there was dark even at noon. Where could he be?
Ans. Tropical evergreen forest.
Q13. A new boy admitted to your class told you that he belong to the state which is home of one horn rhino. For which state he was referring to?
Ans. Assam
3/5 Mark Questions:
Q1. Explain the factors affecting natural vegetation of a place?
Ans.
- Land – nature of land influences type of vegetation as the undulating and rough terrains developed into a variety of natural wildlife as compared to fertile land which undergoes agricultural work.
- Soil – different types of soil support different vegetation. Eg.sandy soil supports thorny bushes where as deltaic soil support mangrove vegetation.
- Temperature- as we can see that tropical area has variety of vegetation as compared to temperate region. Moreover as we go to the higher altitude, vegetation cover changes from temperate forest to grassland to tundra and finally alpine type.
- Precipitation – heavy rainfall areas have generally dense vegetation cover as compared to scanty rainfall areas.
- Sunlight- it is observed that due to longer duration of sunlight trees grows faster in summer as compared to other season of year.
Q2. Differentiate between tropical rainforest and tropical deciduous forest?
Ans.
Tropical evergreen forest
- They are also called Rain forest
- Trees shed their leaves at different types of year.
- They are grown in the areas having warm and wet climate throughout the year.
- They grow in areas having annual rainfall more than 200 cm.
- Vegetation is so dense that even sunlight cannot reach to ground.
- Plant found here are ebony, mahogany, rosewood, rubber etc
Tropical deciduous forest
- They are also called Monsoon forest.
- Trees shed their leaves at the same time of year.
- They are grown in areas where seasonal change occurs with rainfall in summer.
- They grow in areas having annual rainfall of 70 to 200 cm
- Vegetation is not so dense.
- Trees found here are Neem, banyan, Peepal, mango, Sal, Shisham etc
Q3. Write a short note on the diversity of flora and fauna in India.
Ans.
- India has variety of flora and fauna. 89 National Parks, 490 Wildlife sanctuaries and Zoological Gardens are set up to take care of Natural habitat of the fauna, There are 14 biosphere reserves too.
- Five different types of vegetation cover are found here which ranges from rainforest to thorny bushes as well as snow clad alpine vegetation.
- India is rich in its fauna. It has approximately 90,000 of animal species. The country has about 2,000 species of birds. They constitute 13% of the world’s total. There are 2,546 species of fish, which account for nearly 12%
- of the world’s stock. It also shares between 5 to 8 per cent of the worlds amphibians, reptiles and mammals.
- The elephants are found in the hot wet forests of Assam, Karnataka and Kerala
- One-horned rhinoceroses live in swampy and marshy lands of Assam and West Bengal.
- Arid areas of the Rann of Kachchh and the Thar Desert are the habitat for wild ass and camels.Indian bison, nilgai (blue bull), chousingha (four horned antelope), gazel and different species of deer are some other
animals found in India - India is the only country in the world that has both tigers and lions.
- Ladakh’s freezing high altitudes are a home to yak, the shaggy horned wild ox weighing around one tonne, the Tibetan antelope, the bharal (blue sheep), wild sheep, and the kiang (Tibetan wild ass).
- In the rivers, lakes and coastal areas, turtles, crocodiles and gharials are found
- Peacocks, pheasants, ducks, parakeets, cranes and pigeons are some of the birds inhabiting the forests and wetlands of the country.
Q4. What is the need of conserving bio-diversity?
Ans. Every species has a role to play in the ecosystem.
- we have selected our crop from a biodiverse environment.
- we have got too many medicinal plant from this,
- the animals we have as our livestock is also selected from the large variety of fauna,
- Even insect help in pollination which we know is essential,
- how can we forget in the role of microorganism which sustains the flow of energy for our survival.
Q5. List five different types of forest products.
Ans.
- Timber from mahogany, sal, teak trees
- Medicines from Sinchona, Arjun, Neem, Babool tree
- Rubber from the latex of rubber tree
- Wood Pulp are obtained from the softwood trees like spruce, pine, fir for making paper
- Firewood
- Honey etc.
Q6. What are the steps taken by the government to protect wildlife?
Ans. To protect the flora and fauna the government has taken followings
steps-
- Wildlife Protection Act was implemented in 1972 in India.
- Fourteen biosphere reserves have been set up in the country to protect flora and fauna,
- Financial and technical assistance is provided to many Botanical Gardens by the government since 1992
- Project Tiger, Project Rhino, Project Great Indian Bustard and many other eco-developmental projects have been introduced
- 9 National Parks, 490 Wildlife sanctuaries and Zoological gardens are set8 up to take care of Natural habitat of the fauna.
Q7. Describe the variety of vegetation found in different altitude of Himalaya?
Ans.
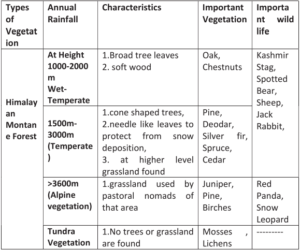
Q8. What are the causes of the depletion of flora and fauna in India?
Ans. Cause of Depletion of flora and fauna are:-
- Hunting of animals by poachers for skin, tusks etc.
- Commercial exploitation of forest products for wood, medicines, paper etc.
- Mining activity
- Pollution due to chemical industrial waste
- Reckless cutting of forest to bring land under cultivation and inhabitation
Q9. What will happen if all the tigers are dead?
Ans.
- If all the tigers are dead at a place it will mean that a part of carnivores are absent.
- it will result in the rise of number of deers, nilgai ,and other herbivore animals.
- with the rise in number they will be forced to move toward human settlement for food and graze the crop.
- this will lead to the scarcity of food for human and may be catastrophic for its existence.
Q10. Distinguish between thorn forests and mangrove forests on the basis of rainfall, vegetation and location.
Ans.
Thorn Forests
- Rainfall:-Rainfall in these types of forests are somewhere 70cm or less.
- Vegetation:- Babool, kiker, palm, cacti and acasia are the main plants.
- Location:- Found in semi-arid regions of Gujrat, Rajasthan, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
Mangrove Forests
- Rainfall:- These types of forests develop in the deltaic region, and does not concern with the rainfall.
- Vegetation:- Sundari is the major tree type in these types of forests. The others are Agar and Korea.
- Location:- They are found in the deltas of Ganga, Mahanadi, Kaveri, Krishna and Godavari.
Q11. Why tropical rain forest is called an evergreen forest.
Ans.
- These forest have plenty of varieties of vegetation .
- These plants shed their leaves at different times of year.
- Thus when one species of plant shed their leaves others still have their leaves intact.
- In this way these forest always look full of greenery, and are so called evergreen forest.
We hope that Class 9 Social Science Chapter 5 (Natural Vegetation and Wild Life) Important Questions in English helped you. If you have any queries about Class 9 Social Science Chapter 5 (Natural Vegetation and Wild Life) Important Questions in English or about any other notes of Class 9 Social Science in English, so you can comment below. We will reach you as soon as possible…