Chapter – 7
Rise of Popular Movements
In this post, we have given the Important Questions of Class 12 Political Science Chapter 7 (Rise of Popular Movements) in English. These Important Questions are useful for the students who are going to appear in class 12 board exams.
| Board | CBSE Board, UP Board, JAC Board, Bihar Board, HBSE Board, UBSE Board, PSEB Board, RBSE Board |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 12 |
| Subject | Political Science |
| Chapter no. | Chapter 7 |
| Chapter Name | (Rise of Popular Movements) |
| Category | Class 12 Political Science Important Questions in English |
| Medium | English |
Chapter 7 Rise of Popular Movements
One Marker Questions
Q1. Who founded the Dalit Panthers ?
Ans. Arjun Dhale, Namdeo Dhasal.
Q2. Give the full form of NFF:
Ans. National Fishworkers Fourm.
Q3. Name the two major dams constructed on the river Narmada.
Ans. Sardar Sarovar Project(Gujarat) and Narmada Sagar Project (Madhya Pradesh).
Q4. State whether the following statement is true of false: The main strength of social movements lie in their mass base cutting across social sections.
Ans. True
Q5. Sunderlal Bahaguna is associated with which social movement?
Ans. Chipko Movement.
Q6. When was the Right to Information Act passed?
Ans. 2005
Q7. What is BAMCEF?
Ans. The All India Backward and Minority Communities Employees Federation founded by Kanshi Ram.(1971)
Q8. Baba Amte is associated with which Movement?
Ans. Narmada Bachao Andolan.
Q9. Put a mark of right or wrong against the following sentence:- Naxalbari movement is a non-party based movement.
Ans. False(X)
Q10. Which of the following state is not benefited by the Sardar Sarovar Dam build on the river Narmada:
- Gujrat
- Rajasthan
- Maharashtra
- Tamil Nadu
Ans. d) Tamil Nadu
Two marker Questions
Q1. Distinguish between party- based movements and non-party based movements.
Ans. Party based movements are based on the ideology of political parties while non party based movements are Independent from party associations and are spontaneous and unorganised.
Q2. What were the main demands of the Chipko Movement?
Ans.
- The villagers demanded that no forest exploiting contracts should be given to outsiders.
- Local communities should have effective control over natural resources like water, land, and forests.
- They also demanded the government to provide low-cost materials to small industries and ensure the development of the region without disturbing ecological balance.
- This movement took up economic issues of landless forest workers and asked for guarantees of minimum wages.
Q3. What were the two issues related to the Sardar Sarovar project?
Ans. Leading activist Medha Patkar warns that Narmada River risks being turned into a lake due to various moves by the government. In addition, illegal sand mining in the catchment area of Sardar Sarovar dam is further increasing the risk of soil erosion, land degradation and habitat loss
Q4. What was the role of Mazdoor Kisan Shakti Sangathan in the enactment of Right to Information Act?
Ans. The Mazdoor Kisan Shakti Sangathan (MKSS) was formed by a group of people in Rajasthan to demand information from the government. The MKSS demanded information to be made available to the public. They questioned the arbitrary decisions of the government and demanded access to documents.
Four Marker Questions
Q1. What do you understand by New Social Movements?
Ans. New social movements have emerged as corrective to new challenges like environmental degradation, violence against women, destruction of tribal cultures and violation or Human Rights, transgender rights etc. They are comprehensive issues affecting a major strata of the society and are issue based seeking redressal within the system.
Q2. What do you understand by party based movements?
Ans. Party based movements have close Association with political pnrtles and follow their objectives and ideologies, well organised and financed by political parties and often have a hidden agenda of opposing the party in power. For ex:- the Indian Independence was fought by the Congress Party, the highly violent Maoist movement.
Q3. What do you understand about the National fishworkers forum led social movement?
Ans. The National Fishworkers Forum owes its birth to the striking Indian fishing communities in 1978. It was a Federation of trade unions and organisations of fishworkers in India. The conflict between the newly introduced large- scale mechanized trawlers and the small-scale traditional fishworkers gave rise to this. In 2008 NFF led a campaign to ‘save the coast and save the fishers’.
Q4. What was naxal movement and where did it start?
Ans. The term naxalites come from Naxalbari, a small village in West Bengal where a section of the Communist Party of India ‘Marxist led by Charu Majumdar initiated an uprising in 1967.
Five Marker Questions
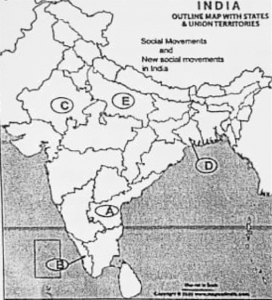
Q1. In the given map of India five states have been marked as A,B,C, D and E. Identify them on the basis of the information given below and write their correct names along with their serial number of the information used and the concerned alphabets.
|
S. No. Of the information used |
Concerned alphabet |
Name of the state |
|
1) |
A |
|
|
2) |
B |
|
|
3) |
C |
|
|
4) |
D |
|
|
5) |
E |
|
i. The state where women put a ban on the sale of arrack and stopped its auction.
ii. The state where the National Fishworkers Forum started its agitation.
iii. The state where the MKSS demanded records for famine relief and accounts of labourers.
iv. The state where the Tebhaga Peasants Movement took place in 1946-47
v. The state which saw a farmer’s agitation in 1988 protesting against the government’s increased electricity rates.
Ans.
|
S. No. Of the information used |
Concerned alphabet |
Name of the state |
|
1) |
A |
Andhra Pradesh |
|
2) |
B |
Kerala |
|
3) |
C |
Rajsthan |
|
4) |
D |
Present day West Bengal |
|
5) |
E |
Uttar Pradesh |
Six Marker Questions
Q1. Do social movements helps make democracy a success? Give your views.
Ans. Popular movements are an integral part of democracy and help to keep the democracy alive. The possibilities of deep social conflicts are reduced by popular movements at same time they make the people aware of their rights. The weak and the marginalised sections of the society get an outlet to assert their democratic rights and place their demands. Most of them usd used peaceful methods of protest such as hartals, rallies picketings etc. Popular social movements bring about positive social changes in the lives of the common people and help to legitimise democracy they are an expression of deprivation, common purpose, solidarities and a common purpose. Rights of the tribal population, displaced people, settlement and compensation issues are safe gaurded by these movements.
Q2. Explain the role of women in successfully voicing their demands through social movements. Give examples.
Ans.
- The Anti- Arrack movement was a spontaneous mobilization of women demanding a ban on the sale of alcohol in their neighbourhoods. Even rural women in remote villages from the state of Andhra Pradesh battled against the liquor Mafia and against the criminal nexus between the mafia and the government during this period. They adopted peaceful means of picketing by surrounding shops. Their successful agitation resulted in the complete Ban of liquor in the state of Andhra Pradesh. The Anti-Arrack movement provided a platform to discuss private issues of domestic violence.
- The Chipko movement was an environmental movement to prevent the cutting down of trees and it demanded that local communities should have control over their natural resources. It started in Uttarakhand in the early 1973 and women participated actively by hugging the trees and not allowing them to be cut. The Nirbhaya Movement in 2012 for the safety of women and prevention of crimes against women.
- Mass movements led by women have focused more on positive change in women’s life giving space for women’s voices to be heard.
Q3. Describe any six factors which made the farmers movement run by Bhartiya Kisan Union as the most popular and successful movement.
Ans.
- The well established farmers of Western Uttar Pradesh and Haryana against the rising price of electricity. They later formed the Bhartiya Kisan Union.
- The BKU was one of the leading farmers organisation. The four main demands were higher government price for sugarcane and wheat, abolition of restrictions on the free movement of farm produce to other states,guaranteed supply of electricity at reasonable rates and waiver of loans, provision of government pension for farmers.
- The B KU organised rallies, demonstrations, sit-ins and Jail Bharo Andolan.The success of BKU lies in the method of organisation adopted by it. It helped to mobilize the people. It was an informal organisation but it sustained for a long time and remained stable because it was based on a clan
- network; they were successful as a pressure group by the sheer strength in numbers.
We hope that Class 12 Political Science Chapter 7 (Rise of Popular Movements) Important Questions in English helped you. If you have any queries about class 12 Political Science Chapter 7 (Rise of Popular Movements) Important Questions in English or about any other notes of class 12 Political Science in English, so you can comment below. We will reach you as soon as possible…